There are so many things to consider during pregnancy from healthy eating to ensuring you are getting proper exercise and rest. Along with changes to diet, hormones, and pant size, pregnancy comes with extra consideration to oral health needs.

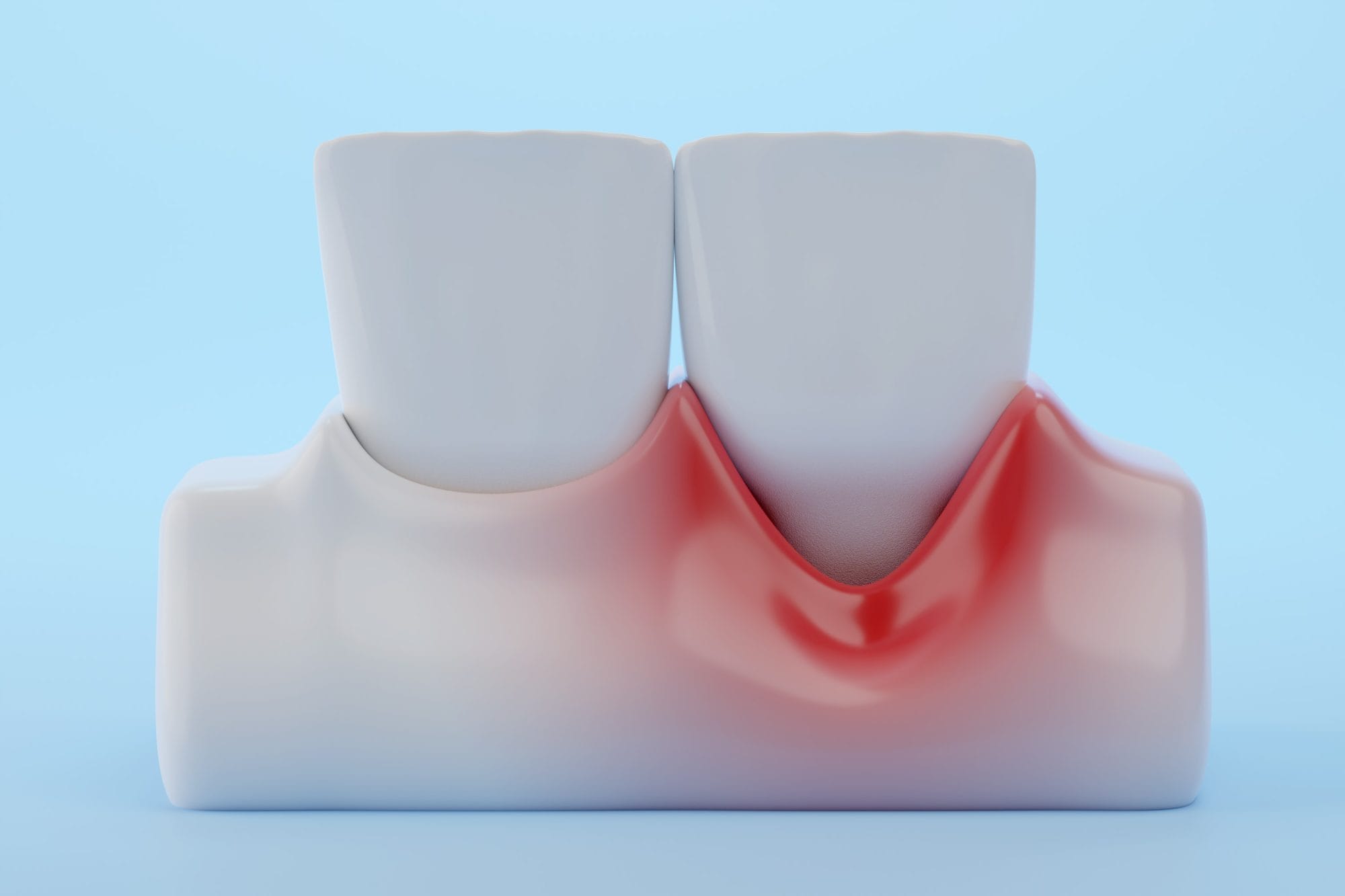
Oral health symptoms related to pregnancy can range from sensitive, bleeding gums to developing pregnancy gingivitis. Pregnancy-related gum disease, also known as pregnancy gingivitis, is when your gums are more sensitive, swollen, red, and irritated. Left untreated, pregnancy gingivitis may progress into periodontitis, which is an infection that affects the bones that hold the teeth in place.
Studies show there are health risks associated with periodontitis during pregnancy. This includes increased risk with delivering a pre-term baby and a baby with a low birth weight. Below we explore the causes of pregnancy-related gum disease and what expectant mothers can do to best take care of their oral health.
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy-Related Gum Disease
Pregnancy gingivitis may develop between the second and eighth month of pregnancy, typically reaching its peak during the third trimester.
Symptoms of gingivitis, whether during pregnancy or otherwise, include tender, puffy gums. Gums may bleed during brushing, flossing and eating. You may notice a bad taste in your mouth and/or bad breath.
Causes of Pregnancy-Related Gum Disease
Hormones
Heightened levels of progesterone and estrogen during pregnancy causes extra blood to flow to the mucous membranes, which may cause swelling and bleeding of the gums.
Changes in diet
During pregnancy, your diet can change significantly. Food cravings for sugary sweets or fast foods may lead to the bacteria that causes cavities to overgrow and out-compete the healthy bacteria in your mouth. Try chewing sugarfree gum for 5-10 minutes after a meal, or eat a piece of cheese to stimulate saliva flow and neutralize acidity. Sip on unflavoured water to rinse your mouth and wash away food debris. Better yet, brush and floss after meals!
Morning sickness
Morning sickness is very common during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. However, this exposes teeth to much higher levels of acid. Acids are harmful to tooth enamel and may lead to tooth decay and acid erosion (wear on the teeth). We recommend you rinse with water after being sick in order to wash these acids off your teeth and help the pH in your mouth recover. Make sure that you wait 1 hour before brushing teeth after any acid challenge like vomiting, as this can wear down your enamel.
Changes to saliva
During pregnancy saliva composition may change. For some, saliva may be more acidic during pregnancy. For others, saliva production may be reduced. Mineral compounds in saliva may decrease during pregnancy. These factors can lead to increased plaque buildup, higher levels of bacteria, and risk of tooth decay and erosion.
How to prevent pregnancy-related gum disease
See your dentist
The first step to prevention of pregnancy-related gum disease is a thorough cleaning and checkup with your dentist. During the first trimester, visit your dentist for a full assessment. Let them know of your pregnancy, so that they may diagnose any existing dental issues and recommend an oral hygiene routine to follow throughout your pregnancy. It is strongly recommended that you have your teeth professionally cleaned during your second trimester. Most dental treatment is safe during pregnancy.
Practice great oral hygiene
In addition to stepping up on baby-minded healthy choices, make sure to have a great daily oral hygiene routine. This is beneficial for expecting mothers and their unborn babies. Choose a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean those potentially sensitive gums and teeth. If pregnancy is causing odor sensitivities, ensure to find mild, appealing toothpaste to make oral hygiene during pregnancy as pleasant as possible. Brush teeth for 2 to 3 minutes gently at least twice a day and floss at least once a day.
Eat a healthy diet
A diet rich in calcium, minerals, proteins, vitamins A, D, and K, as well as plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables may help reduce oral health issues during pregnancy.
Drink water
Staying well hydrated through all phases of pregnancy is recommended and goes a long way to protect oral health. Drinking water after snacks and meals can help keep the mouth fresh and wash away food debris. It also helps the buffer the pH in your mouth and prevent cavities.
Fortunately, pregnancy gingivitis and other pregnancy-related oral health issues generally cease with the arrival of the baby. Developing great oral health habits during pregnancy helps to minimize pregnancy-related gum disease. It also goes a long way towards creating oral health habits that carry on after pregnancy.
Did you know that the bacteria in the mother’s mouth generally transfers to baby by the age of 18 months? This is even more motivation to keep good oral health habits and ensure you have healthy bacteria in your mouth to pass onto your baby.
We’d like to hear from you
Do you have any questions about dental care during pregnancy? Or do you have a question about gum disease that you would like to share? We welcome you to post any questions, comments, or thoughts below.

Leave A Comment